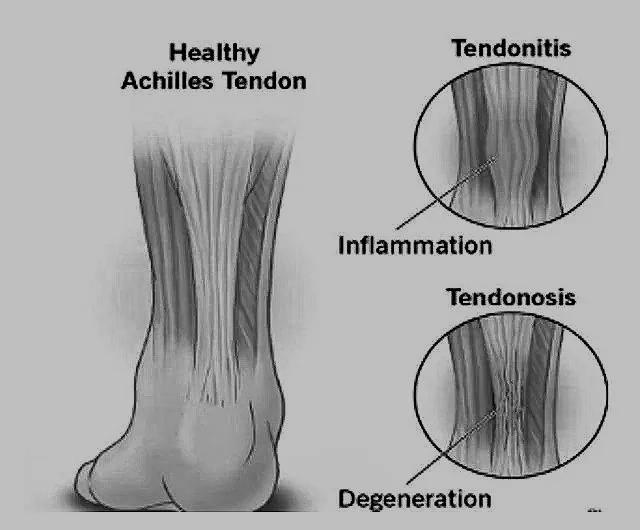
TENDINITIS VS TENDINOSIS |
TENDINITIS VS TENDINOSIS |
Not all painful tendons are the same! Some tendons bear heavy load like the Achilles tendon while others are more delicate, assisting with fine movements of the toes. Since not all tendons are the same, not all tendons should be treated the same. Your treatment plan may differ based on which condition you are experiencing.
TENDINITIS VS TENDINOSIS
Tendinitis is inflammation of a tendon. Inflammation is your bodies response to injury. Tendinitis is usually triggered by repetitive motion or stress causing micro-tears of the tendon. Tendinitis can also be caused from a direct injury to the tendon or from heavy load. Continued or excessive use of an inflamed tendon can cause further inflammation to the tendon leading to more pain and damage.
Tendinosis is chronic degeneration of tendon. This type of damage is caused by long term (chronic) tendon injury that has not properly healed. Immature connective tissue (Type III collagen) can invade an injured tendon causing irregularity and increased thickness in the native tendon. This can create weakness in the tendon by disrupting healthy, mature type I collagen fibers eventually leading to increased swelling, pain, or even tendon rupture.
SYMPTOMS
TENDINITIS
🔵 Pain: Sharp or localized pain, typically worse during or immediately after activity.
🔵Swelling: Visible or palpable swelling around the tendon due to inflammation.
🔵 Warmth and Redness: The affected area may feel warm or look red.
🔵 Tenderness: The tendon is tender to touch.
🔵 Stiffness: Mild stiffness, especially after inactivity or in the morning.
🔵Function: Pain may limit the range of motion temporarily but typically does not cause long-term deficits.
TENDINOSIS
🔵 Pain: Persistent, dull, or aching pain that worsens with prolonged activity or use.
🔵 No Swelling: Generally, no inflammation; instead, the area may feel thickened or firm due to degenerative changes.
🔵 Nodules: May develop small lumps or nodules along the tendon due to collagen disorganization.
🔵 Tenderness: Chronic tenderness along the tendon, often at the attachment point to the bone.
🔵 Stiffness: Stiffness and reduced flexibility, particularly during or after activity.
🔵 Function: Gradual decline in tendon strength, increasing risk of rupture or impaired performance over time.
CAUSES & RISK FACTORS
TENDINITIS
CAUSES
🔵Overuse or Repetitive Motion: Sudden or excessive strain on a tendon (e.g., running, jumping).
🔵 Acute Injury: Trauma to a tendon during physical activity.
🔵Improper Technique: Poor form during exercise or sports.
🔵Sudden Increase in Activity: Rapidly starting or intensifying a workout routine.
🔵Inappropriate Footwear: Wearing shoes that lack proper support.
RISK FACTORS
🔵High-Impact Activities: Sports like basketball, tennis, or running.
🔵Occupational Strain: Jobs involving repetitive movements or prolonged standing.
🔵Tight Muscles: Calf or hamstring tightness increases tendon stress.
🔵Age: Tendons lose flexibility with age, increasing susceptibility to inflammation.
🔵Systemic Conditions: Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout can predispose to tendon inflammation.
Examples of activities that can lead to tendinitis in the foot/ankle include:
🔹Sports/Exercise: Driving, walking, running, jumping, hiking, dancing, sporting activities, high-impact workouts and Inadequate stretching/warm up
🔹Occupational/Daily Strain: Prolonged standing, heavy lifting, or repetitive motions.
🔹Footwear Issues: Walking barefoot, sandals/flipflops, wearing poorly fitted shoes.
🔹Improper Technique: Poor form, sudden activity increases, or overtraining.
🔹Biomechanical/Risk Factors: Overpronation, acquired flatfoot or congenital flatfoot deformities, or tight calf muscles, rolling ankle/sprain.
TENDINOSIS
CAUSES
🔵Chronic Overuse: Long-term repetitive strain without sufficient rest (e.g., distance running).
🔵Untreated Tendinitis: Inadequate healing from acute inflammation can lead to degeneration.
🔵Age-Related Degeneration: Tendon fibers weaken and lose elasticity over time.
🔵Poor Biomechanics: Structural abnormalities like flat feet or overpronation increase tendon stress.
RISK FACTORS
🔵Prolonged Stress: Long-term participation in high-impact or repetitive activities.
🔵Insufficient Recovery: Lack of rest between strenuous activities.
🔵Weak Tendons: Previous injuries or inadequate strengthening exercises.
🔵Footwear: Consistent use of flat shoes or high heels.
🔵Comorbid Conditions: Poor circulation, diabetes, or obesity exacerbate tendon degeneration.
Examples of activities that can lead to tendinosis in the foot/ankle include:
🔹Repetitive Strain: Long-distance running, walking, or cycling without rest.
🔹Sports/Exercise: High-impact sports, jumping, or dance with sustained tendon stress.
🔹Occupational Strain: Prolonged standing or repetitive weight-bearing tasks.
🔹Overuse/Improper Technique: Overtraining, poor form, or overloading tendons.
🔹Footwear Issues: Unsupportive shoes or high heels.
🔹Biomechanical/Risk Factors: Overpronation, acquired flatfoot or congenital flatfoot deformities, or tight calf muscles, rolling ankle/sprain, aging, or unresolved tendinitis.
Summary Table
TENDINITIS TENDINOSIS
Primary cause Acute overuse or trauma | Chronic overuse or degenerative changes
Onset Sudden | Gradual
Risks factors High-impact activities, age, tight muscles | Prolonged stress, age, untreated tendinitis
Underlying process Inflammation | Collagen breakdown and degeneration
DIAGNOSIS & TESTS
🟦History and Physical Examination
🔹Symptom Onset: Sudden onset of pain after recent activity or trauma.
🔹Pain Characteristics: Sharp, localized pain that worsens with movement or pressure.
🔹Swelling and Redness: Common in acute inflammation.
🔹Tenderness: Pain on palpation over the affected tendon.
🔹Range of Motion: Painful but generally preserved.
🟦Tests
🔹Clinical Maneuvers:
Pain during resistance testing or specific movements of the affected tendon.
🔹Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound: Shows thickening, fluid around the tendon, or hypervascularity indicating inflammation.
MRI: May reveal tendon thickening or surrounding inflammatory changes.
🟦 History and Physical Examination
🔹Symptom Onset: Gradual, persistent pain or stiffness over weeks to months.
🔹Pain Characteristics: Chronic, dull, or aching pain, often aggravated by prolonged activity.
🔹Thickened Tendon: Nodules or firm areas may be palpable along the tendon.
🔹Reduced Flexibility: Limited range of motion and stiffness.
🟦 Tests
🔹Clinical Maneuvers:
Pain or stiffness on resisted movement, often without significant swelling.
🔹 Imaging Studies:
Ultrasound: Reveals hypoechoic (dark) areas, irregular tendon structure, and reduced vascularity in advanced cases.
MRI: Shows tendon degeneration, collagen disorganization, and potential partial tears.
Histological Examination (rarely performed): Confirms collagen degeneration and absence of inflammatory cells.
MANAGEMENT & TREATMENT
Early stages of tendinitis treatment may include the following:
🟦Anti-inflammatories: NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti- inflammatory) like ibuprofen or naproxen. You may be prescribed additional medications to help with
inflammation and/or pain. These medications are designed to reduce the swelling in and around the tendon by reducing the inflammatory response of your body.
🟦 Ice: Ice massage or ice bath 15-20 minutes several times daily.
🟦 Rest: This may include immobilization, taping, padding, reducing the impact and/or repetition of activity, or even completely keeping weight off of the foot as instructed by your physician.
🟦 Compression: A compression wrap, compression sleeve, compression stocking, or ace bandage can help reduce swelling in and around the tendon improving normal architecture to expedite proper healing of the tendon.
🟦 Physical therapy: Therapy may be recommended to assist with your return to activity to help prevent re-injury or to assist with tendon healing.
Recommendations to prevent re-injury:
🟦 Physical therapy and exercise to improve tendon strength, motion.
🟦 Custom vs. over-the-counter orthotics may be recommended to improve stability to prevent re-injury.
🟦Occasionally surgical intervention may be discussed or recommended based on the severity of the tendon injury or issue causing the continued tendon injury.
Early treatments of tendinosis may include:
🟦 Immobilization: This may include casting, taping, padding, heel lifts, reducing the impact and/or repetition of activity, or even completely keeping weight off of the foot as instructed by your physician.
🟦 Ice: Ice massage or ice bath 15-20 minutes several times daily.
🟦 Physical therapy: Therapy is designed to help your body repair and replace immature scar tissue in the diseased tendon with health mature tendon, reduce pain, and aid in return to activity.
🟦Stretching: You will be directed by your treating physician and/pr physical therapist on appropriate stretches to help improve tendon healing.
🟦 Massage: Ice massage or manual massage can help break down immature scar tissue and assist with correct tendon healing.
Later treatments of tendinosis may also include:
🟦 Weight training: Under the direction of your physician and/or physical therapist you may be directed on appropriate strengthening of tendon/muscle to assist with tendon healing, recovery, and to minimize risk of re-injury.
🟦 Improve stability: Custom vs. over-the-counter orthotics may be recommended to improve stability if a tendon is predisposed to re-injury.
🟦 PRP injection: Platelet Rich Plasma Injection therapy helps guide your body’s own repair process using specific proteins in your own blood. Platelet rich plasma is injected into the site of damage, providing growth factors and proteins to stimulate repair. This procedure can be done in the office. This option is often recommended to avoid the need for surgical intervention.
🟦 Surgery: If all nonsurgical options have been exhausted and your tendon injury is still preventing you from performing your normal activities, surgery may be considered. Additional imaging (MRI/Ultrasound) may also be order to guide you and your physician in choosing appropriate interventions throughout your treatment plan.
🟦 Nutrition: Change to your diet may improve collagen production and improved tendon health. Nutrients linked to tendon health include vitamin C, manganese, zinc, vitamin B6, and vitamin E.
PREVENTION
🟦 Avoid Overuse:
Pay attention to early signs of pain or discomfort and rest as needed.
🔹 Manage Acute Strain:
Address minor injuries immediately to prevent escalation.
🔹 Ice After Activity:
Use cold therapy to reduce inflammation after repetitive activities.
🟦 Prevent Chronic Stress:
Avoid prolonged repetitive activities without breaks.
🔹 Focus on Recovery:
Incorporate adequate recovery time and cross-training to minimize repetitive strain.
🔹 Maintain Tendon Health:
Ensure adequate nutrition, especially protein, vitamin C, and collagen-promoting nutrients.
PROGNOSIS
🟦 Tendinitis: Acute Condition
🔹Prognosis: Generally good with timely and appropriate treatment. Most cases resolve within a few weeks to months.
🔹Recovery Time: Shorter recovery period (typically 4-6 weeks) if the condition is managed early.
🔹Outcomes: Inflammation and pain usually subside completely with rest, anti-inflammatory measures, and physical therapy.
🔹Complications: Delayed or insufficient treatment can lead to chronic tendinosis.
🟦 Factors That Improve Prognosis:
🔹Early detection and intervention.
🔹Avoidance of aggravating activities during recovery.
🟦 Tendinosis: Chronic Condition
🔹Prognosis: Variable, depending on the severity of degeneration and adherence to treatment. Complete healing may take several months (3-6 months or longer).
🔹Recovery Time: Longer due to the need for collagen remodeling and tendon regeneration.
🔹Outcomes: While pain and function can improve significantly with eccentric exercises, physical therapy, and regenerative treatments (e.g., PRP therapy), the tendon may not fully return to its pre-injury state.
🔹Complications: If untreated, tendinosis can lead to permanent weakness, reduced function, and a higher risk of tendon rupture.
🟦 Factors That Improve Prognosis:
🔹Compliance with long-term rehabilitation programs.
🔹Use of advanced therapies (e.g., shockwave therapy or platelet-rich plasma).
🔹Avoiding repeated overuse during recovery.
"Understanding the differences between tendinitis and tendinosis is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Whether you are managing acute inflammation or chronic tendon degeneration, early intervention and guided care can help restore mobility and improve quality of life. Consult a healthcare professional for tailored advice and treatment options."